Tag: Gandhi
-
Political Dimension of Hindutva, Part 13 Introduction – A Justification of “Relative Violence” Violence and non-violence have long been central themes in Indian philosophical and political thought. Vinayak Damodar (Veer) Savarkar, a key proponent of Hindutva, presented a unique discourse on the subject, arguing for a pragmatic approach to violence—what he termed “just, relative violence.”…
-
Political Dimension of Hindutva, Part 12 Introduction – Savarkar’s Radical Philosophy of Resistance Few statements in modern Indian political thought are as provocative as Vinayak Damodar (Veer) Savarkar’s declaration that relative non-violence is a virtue, absolute non-violence a crime. This concise yet explosive maxim captures the essence of Savarkar’s departure from the dominant ‘Gandhian ethos’…
-
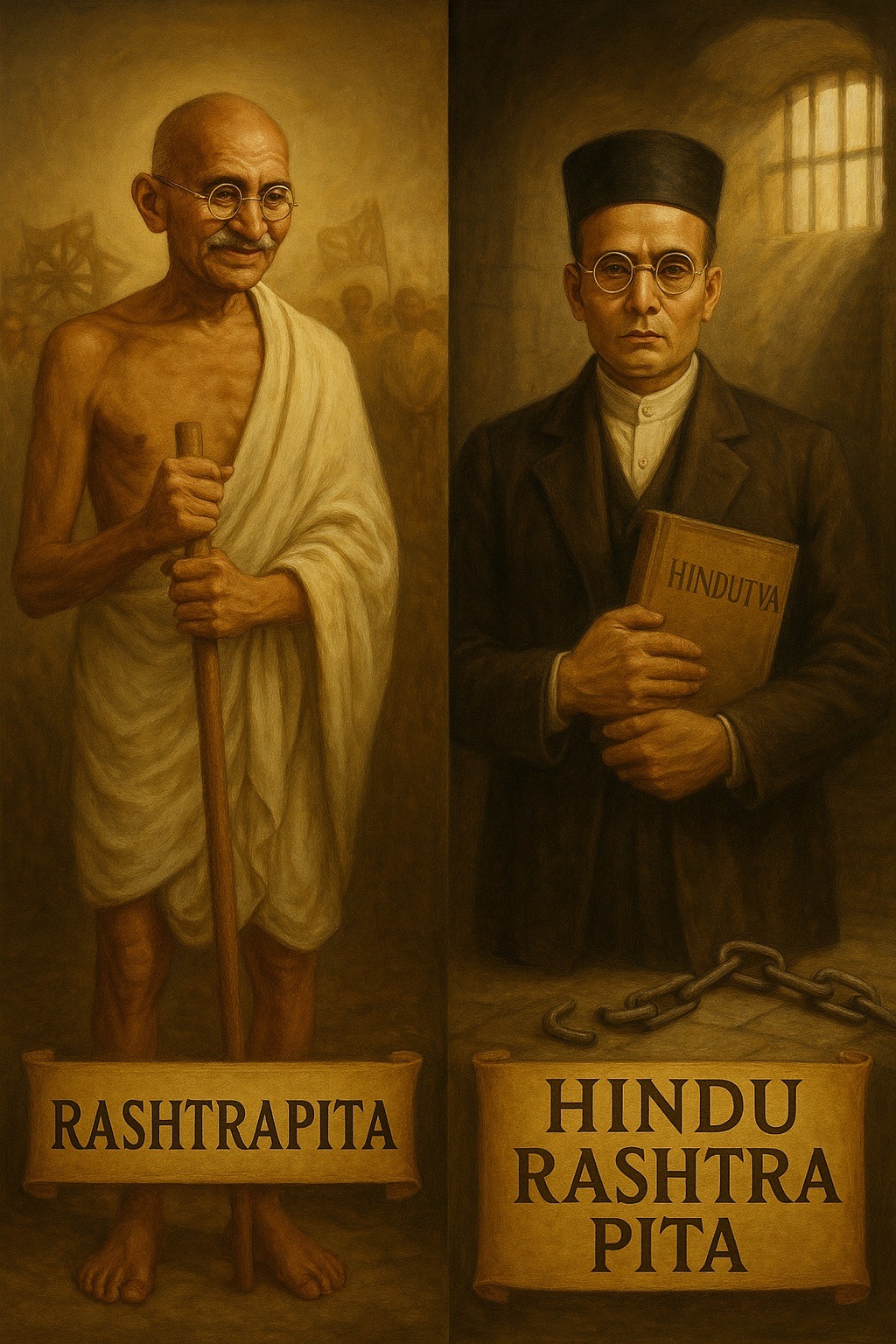
Since M.K. (Mahatma) Gandhi is called by many of his followers Rashtrapita (“Father of the Nation”), it is fitting that Vinayak Damodar (Veer) Savarkar be acknowledged as Hindu Rashtra Pita—the “Father of the Hindu Nation.” This title recognizes not only his seminal contribution to the Indian freedom struggle but also his immense personal sacrifices and…
-
Economic Dimension of Hindutva, Part 6; Savarkar’s Economic Principles (2/13) Vinayak Damodar (Veer) Savarkar was not just a political thinker and revolutionary; he was also a strong advocate for technological progress. At a time when Indian society was grappling with the impact of modernization, Savarkar made a passionate appeal to his compatriots to welcome the…